He was a little tired, climbing the stairs. Brushed it off as age. A week later, watching TV, he felt it again: some tightness in the chest, a little shortness of breath, nothing too dramatic. He ignored it. Months later, his routine health check found something surprising: he’d already had a heart attack, and not just any heart attack, but a silent one.
Silent heart attacks don’t make headlines like the big ones you see in movies. They creep in quietly, without the classic chest pain or warning signs. Many people go about their lives without ever realizing that their hearts have already been damaged.
This blog provides details about what a silent heart attack is, why it occurs, and how you can tell if these hidden symptoms are happening to you – and how you can prevent it (even if “you feel perfectly fine”). Because when it’s your heart, silence is never golden.
What is a Silent Heart Attack?
A silent heart attack occurs when blood flow to a section of the heart becomes blocked for a short time or partially, damaging the heart muscle, but does not cause chest pain typical of a classic heart attack.
It’s a Silent Myocardial Infarction (SMI) in medical terminology.
While a typical heart attack feels like a visible storm, a silent one is more like a quiet thunder; you may not notice it at all.
According to the American Heart Association, about 1 in 5 heart attacks in the US are silent. In fact, a group of cardiologists estimates that up to 45% of cardiac events in India may be silent. That means many people walking among us may have experienced a heart attack and don’t even know it.
Why Does a Silent Heart Attack Go Unnoticed?
There are many reasons a person might have a silent heart attack, but most experts believe it occurs when:
- The pain signals are too subtle or misinterpreted as something else, such as gas, fatigue, or muscle ache.
- Some people are highly tolerant of pain and dismiss the symptoms.
- Diabetic patients often have nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy), which dulls pain sensations, making it harder to detect chest pain.
They go on about their day, unaware that their hearts are in distress.
Silent Heart Attack Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
While a classic heart attack may bring on sharp or crushing chest pain, symptoms of this so-called “silent” heart attack might be so mild that they are often brushed off. But those “silent” signs are your body’s distress signals, and you should never ignore them.
4 signs of a silent heart attack:
- Unexplained fatigue: Feeling overly tired even after very little movement or relaxation.
- Mild chest pressure: A dull heaviness or tightness in the chest, not painful.
- Shortness of breath: Particularly when you climb stairs or walk short distances.
- Pain in the jaw, back, or neck: The ache might move instead of focusing on the chest for no apparent reason.
Other mini heart attack symptoms or mild heart attack symptoms may include:
- Indigestion or heartburn-like pain
- Nausea or dizziness
- Sweating without reason
- Uneasiness, anxiety, or sudden weakness
If you’ve felt any of these and brushed them off, it’s time to get checked, because your body could be trying to tell you something really important.
How Does a Heart Attack Happen?
Your heart requires oxygen-rich blood to do its job. When cholesterol and fat accumulate in the arteries (in a process known as atherosclerosis), blood flow is blocked.
This blockage deprives the heart muscle of oxygen, damaging tissue. If the blockage is partial and short-lived, the symptoms may be mild or silent, but the damage is still real.
Over time, these silent episodes weaken the heart and increase the risk of a major attack later.
Who Is at Risk of a Silent Heart Attack?
Anyone could have one, but some people face a higher risk:
- Diabetics (decreased sensitivity of nerves)
- Women (often experience atypical symptoms.)
- Elderly adults
- Smokers
- Individuals with high blood pressure or cholesterol
- Those with a sedentary lifestyle or obesity
Dr Bimal Chhajer, Founder, SAAOL Heartcare, shares:
“Many patients think a heart attack has to hurt. But the ones that surprise us are silent heart attacks, they’re quiet but just as deadly.”
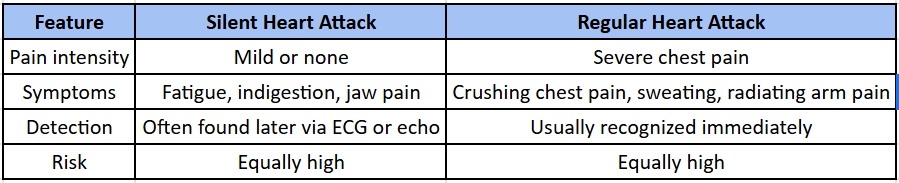
Silent Heart Attack vs Regular Heart Attack
Why Silent Heart Attacks Are Dangerous
Because they go unnoticed, treatment is delayed.
By the time physicians find it (often with an ECG, echocardiogram, or stress test), damage may already have been done to that muscle.
This increases the risk of:
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- Another major heart attack
Silent Heart Attack Causes
A silent heart attack is just another type of heart attack, and its causes are the same as those of other types.
- Blocked arteries (atherosclerosis)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Obesity and inactivity
- Stress and poor diet
These risk factors harm your arteries silently, until one day, your heart sends a quiet warning.
How Do Doctors Diagnose a Silent Heart Attack?
“Silent” heart attacks are typically uncovered during a routine check-up or test for what appears to be an unrelated health problem. Tests may include:
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) – This is used to find out the heart muscle damage.
- Echocardiogram (Echo) – Measures the pumping function of your heart.
- Blood tests (Troponin, CK-MB) – Identify cardiac enzyme level post injury.
- Stress Test or CT Angiography – Can detect clogged arteries.
If you’ve ever had unexplained fatigue, breathlessness, or minor discomfort in your chest, these tests are worth getting done, especially if you have risk factors.
Non-invasive Treatment Options for Silent Heart Attack

EECP Treatment
At SAAOL Heartcare Delhi, Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) treatment is the most effective non-invasive way to increase blood flow and open up natural bypasses around narrowed or blocked arteries without surgery. You can find a guide to EECP treatment, in which you can get to know how it can restore oxygen supply to the heart and ease chest pain, even in patients who are not candidates for angioplasty or bypass.
SAAOL Detox Therapy
SAAOL Detox Therapy is designed to remove toxins, heavy metals, and waste from the system, thus promoting better circulation and heart function.
Diet Consultation
Eating a heart-healthy diet that’s low in salt and sugar and high in plant-based foods and is prepared through Zero-oil cooking can prevent the next one. SAAOL has registered expert dietitians who design individualized plans for all the patients.
Stress Management & Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes like daily walking, meditation, adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking or alcohol dramatically reduce the chances of another heart event.
How to Avoid a Silent Heart Attack
Here are some things you can do from today:
- Consume a heart-healthy diet (whole grains, millets, fruits, vegetables)
- Exercise regularly
- Practice meditation or yoga to reduce stress
- Control your blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol
- Get regular heart checkups even if you feel fine
And remember: Prevention is quieter than any cure but stronger.
Conclusion
Listen To Your Heart When It Whispers
A silent heart attack doesn’t have the same symptoms as a typical heart attack, but it can still be detected. Listening early can change everything.
At SAAOL Heartcare Delhi, we believe that awareness, prevention, and the right non-invasive therapies can turn fear into freedom.
Your heart speaks softly, but truthfully. Don’t wait to listen.
FAQs
- What is a silent heart attack?
A silent heart attack, or silent myocardial infarction, happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked but shows few or no typical symptoms like severe chest pain.
- What are the 4 silent signs of a heart attack?
Unusual fatigue, mild chest pressure, shortness of breath, and jaw or back discomfort.
- How is a silent heart attack diagnosed?
Through ECG, echocardiogram, blood tests, or CT angiography.
- Can a silent heart attack be treated?
Yes. Non-invasive treatments include EECP therapy, lifestyle changes, detox therapy, and heart-healthy diet consultation.
- What is the recovery time after a silent heart attack?
It varies by severity but typically requires 6–12 weeks of consistent cardiac care and supervised rehabilitation.