TL;DR
Heart attack vs cardiac arrest are different from each other. A heart attack is caused by blocked blood flow to the heart, while cardiac arrest happens when the heart’s electrical system suddenly stops. Both are medical emergencies, but need different responses. Knowing the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest can help you act quickly and save a life. EECP therapy is a non-surgical option that supports heart health and may help reduce the risk of heart attacks.
He had multiple heart attacks and later died due to cardiac arrest. Hearing this, when an IT professional said “they’re the same thing”, it revealed that many do not know the difference. The difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest is one of the topics not easy to understand in heart health. We often interchange these two terms, but medically, they are far apart from each other.
One is a problem with blood flow. The other is a sudden failure of the heart’s electrical system. Yet both can be fatal. And both demand completely different emergency responses.
So if you’ve ever wondered “are heart attack and cardiac arrest the same?”, or searched for cardiac arrest vs heart attack, you’re in the right place. In this blog, we’ll know the difference between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest in the simplest way possible, just to gain a clear understanding that could one day save a life. We’ll also explore EECP therapy, a painless and non-surgical treatment option that helps improve heart health and may reduce the risk of these heart problems.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack happens when blood cannot reach the heart properly because a blood vessel gets blocked by fat or a clot, medically known as plaque. When this happens, the heart does not get enough oxygen. Without oxygen, part of the heart muscle gets damaged, which can be very dangerous if not treated quickly. The patient suffers from persistent chest pain associated with cold sweats, tiredness, and arm or back pain that does not go away or increases with time.
What is Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest happens when the heart stops beating because its electrical system stops working properly. The electrical system controls the rhythm of the heart. As the system stops, the rhythm stops. In this situation, the heart cannot pump blood to the brain and body, and the patient collapses and loses consciousness immediately. It can also occur due to any pre-existing heart problems,due to drug overdose, any serious physical injury or a sodium-potassium imbalance of the body that has been ignored for a long time.
Cardiac arrest is an extremely serious condition. Immediate attention is necessary to save the patient.
The Difference Between a Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
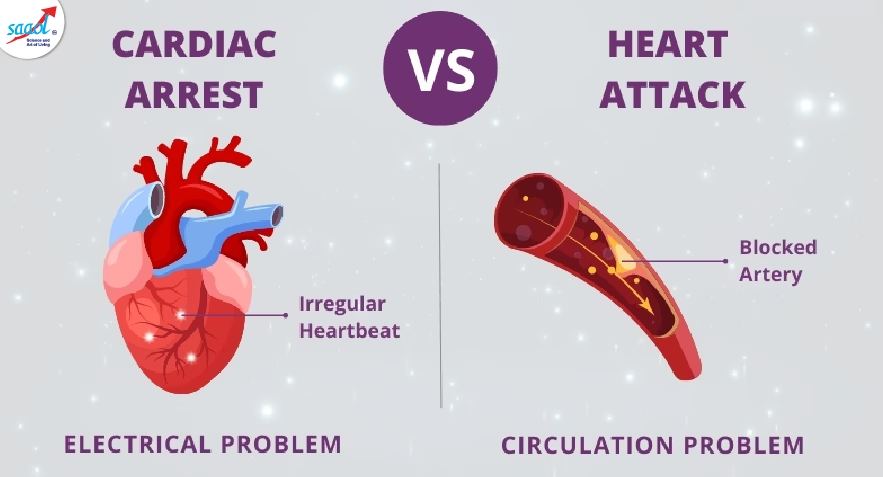
Both heart attack and cardiac arrest affect the heart. In both cases, the heart cannot deliver enough blood and oxygen to the body, making them life-threatening emergencies.
Now, a heart attack is mainly a condition that involves blood circulation, where blood flow to the heart is reduced or blocked, but the heart usually continues to beat. In contrast, cardiac arrest is caused by an electrical failure in the heart, making it stop beating suddenly and without warning, which immediately cuts off blood flow to the body.
In a heart attack, the damage happens slowly over minutes or hours, but in cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly stops beating right away.
Heart Attack Vs Cardiac Arrest (Comparison Table)
Knowing the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest is important because they require different emergency actions and treatments. The table helps you clearly understand the differences at a glance so you can respond correctly and save a life.
| Feature | Heart Attack | Cardiac Arrest |
| Cause | Blocked blood flow in the coronary arteries | Electrical malfunction in the heart rhythm |
| Nature of the Problem | Circulation issue | Electrical issue |
| Onset | Gradual or sudden | Sudden and abrupt |
| Consciousness | Usually conscious | Instant loss of consciousness |
| Pulse | Present (may be irregular) | Absent |
| Breathing | Often still breathing | Not breathing or gasping |
| Emergency Reaction | Call emergency services | CPR + AED + emergency services |
| Can it be Fatal? | Yes | Yes |
Causes of Heart Attack
A heart attack happens because of certain causes, which include the following:
High cholesterol: Unhealthy fats build up (cholesterol), which can narrow the inner walls of the arteries, increasing the chance of blockage.
High blood pressure: If the blood pressure is high, the artery walls weaken over time, causing heart-related problems.
Smoking: Smoking can harm blood vessels and lower oxygen levels, putting extra pressure on the heart.
Sedentary lifestyle: Low physical activity slows down circulation and increases the risk of weight gain and heart problems.
Family history: According to the National Library of Medicine, A genetic history of heart disease can increase the risk of the same for the next generation.
Also read: Why are heart attacks rising in young Indians?
Causes of Cardiac Arrest
The causes of cardiac arrest are:
Abnormal heartbeats: When the rhythm of the heart becomes dangerously irregular, it may suddenly stop pumping blood.
Weak or damaged heart: A previously damaged heart is weak and may fail to function properly and can cause a sudden cardiac arrest without any warning.
Mineral imbalance in the body: Sudden changes in salts like potassium or sodium can disrupt the heart’s electrical signals.
Sudden oxygen shortage: Conditions that cut off oxygen, such as choking or severe breathing problems, can cause the heart to stop.
Physical injury: Major accidents or strong blows to the chest can interfere with the heart’s normal function.
Reaction to drugs or toxins: Some drugs can interfere with the heart’s control system and cause it to shut down abruptly.
What Happens to the Body During a Heart Attack?
The symptoms of a heart attack could be intense chest pain that spreads to the arms, neck, back, and jaw.
Along with shortness of breath, nausea, and sometimes associated with cold sweats, the patients remain conscious and can speak.
During a heart attack, you’re in pain and feeling very unwell, but your heart is still beating and pumping blood, which means you may remain conscious and able to talk or ask for help.
What Happens to the Body During Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest is a sudden collapse. The patient does not have a pulse, does not breathe, or gasp.
During cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly stops beating, causing an immediate shutdown of blood flow to the brain and body, resulting in instant unconsciousness and is life-threatening without quick help.
Note: A heart attack can cause cardiac arrest, but not every cardiac arrest is caused by a heart attack. 
Treatments of Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
What should you do during a Heart Attack?
If you suspect a heart attack:
- Call emergency services immediately
- Chew an aspirin (if not allergic)
- Get to a hospital fast
- Further treatment Options:
Emergency medicines: Doctors give medicines to thin the blood, reduce pain, which helps prevent further clot formation.
Clot-removal treatment: Special drugs may be used to break down the blood clot that is blocking blood flow to the heart.
EECP Treatment: The safest, non-invasive treatment. Inflatable cuffs are used to improve blood flow to the heart and enhance the overall circulation.
Angioplasty: A thin tube with a small balloon is inserted into the artery, which helps to open the blocked artery.
Stent placement: A small mesh tube is placed inside the artery. The mesh helps the block to open, and this also prevents future blockages.
Bypass surgery: In case of complete blockage or any emergency circumstances, surgeons create a new path for blood to flow around blocked arteries.
Ongoing lifestyle care: After treatment, patients are advised to follow a heart-healthy diet, exercise, and medication plan to prevent another attack. Also hearth health should be monitored time to time.
What should you do during a cardiac arrest?
- Call up emergency help
- Start CPR immediately
- Give an AED if available (Automated External Defibrillator)
Further treatment Options:
Chest compressions: Intense pressing on the chest, known as cardiopulmonary resuscitation in medical terms helps push blood to the brain and organs when the heart has stopped.
Electric shock to restart the heart: An electric shock from a defibrillator is used to restart the heart.
Life-saving injections: There are emergency drugs that are administered to help the heart respond and improve blood flow during resuscitation.
Artificial Breathing: Artificial breathing is tried with oxygen or machines to help the person breathe and ensure the body gets enough oxygen to survive.
Intensive hospital care: Once the heartbeat returns, the patient is kept under close medical supervision to prevent repeat episodes.
Treating the pre-existing issues: Doctors focus on treating the main cause, such as rhythm problems or heart disease, to reduce future risk.
It is necessary to treat a cardiac arrest patient immediately. According to the American Heart Association, cardiac arrest impacts thousands of people each year, with nearly three out of four death cases happening at home.
Why is EECP recommended as a better treatment option?
EECP is an affordable, non-surgical treatment that does not require hospital admission, offers long-lasting benefits, and does not disturb daily routines.
EECP helps reduce the future risk of both heart attack and cardiac arrest by improving overall blood circulation and strengthening heart function. The therapy encourages the formation of new blood vessels, so the heart receives a better oxygen supply even if some arteries are partially blocked. This reduces strain on the heart, helps control chest pain, supports healthier heart rhythms, and improves the heart’s ability to work efficiently. When the heart functions well, there are fewer chances of any serious heart problems like a heart attack or cardiac arrest.
At SAAOL Heart Center, advanced non-invasive EECP therapy is offered to support better heart health. With a strong focus on patient care and proven outcomes. Dr. Vishal Sharma, COO, Senior Heart Specialist, SAAOL Heartcare Delhi, says:
“EECP gives the heart a second chance; it restores natural blood flow without surgical risk. Many patients experienced increased energy and less chest pain within weeks.”
The Final Insight
Understanding the cardiac arrest and heart attack difference isn’t medical trivia; it helps you recognize emergencies and respond in time. A quick reaction can save the heart muscle during a heart attack. Fast action saves life in cardiac arrest. Both conditions are medical emergencies requiring urgent help, but the right intervention makes all the difference.
If you or any of your loved ones is suffering from any heart-related symptoms, schedule an appointment and visit the SAAOL Heart Center for a personalized consultation. Start your journey toward better heart health today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can cardiac arrest happen without a heart attack?
Yes, cardiac arrest can happen even if a person has never had a heart attack. It can occur when the heart’s electrical system suddenly stops working properly, and this is not always related to a heart attack or blocked arteries.
Q2. Is sudden cardiac arrest always fatal?
No, sudden cardiac arrest is not always fatal. A person can survive if CPR is started immediately and a defibrillator (AED) is used quickly, as these help keep blood flowing and restart the heart until medical help arrives. According to the American Heart Association, the right and immediate CPR can double or triple the survival rate.
Q3. How do I know if it’s a heart attack or cardiac arrest?
A heart attack causes chest pain and other physical discomfort. The patient remains conscious, the heart still beats. Cardiac arrest causes sudden collapse and unconsciousness. The heart stops beating.
Q4. Can young people get cardiac arrest?
Yes. Even young people can suffer sudden cardiac arrest due to heart rhythm problems, hidden heart conditions, genetic disorders, severe electrolyte imbalance, drug use, unhealthy eating habits or extreme physical stress.
Q5. What should I do if someone collapses suddenly?
Call emergency services immediately if a person collapses and start CPR right away. An effective CPR can save a life. If available, use a defibrillator (AED) to restart the heart.


